- +91 93594 94102
- +91 63775 93771
-
Amrit Hospital, Gandhi Colony, Rudrapur
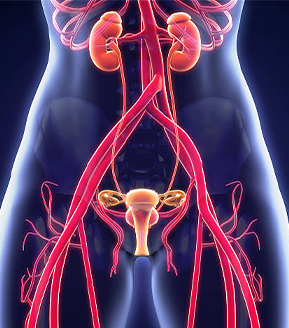
Female Urology
The subspecialty of female urology is concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of urinary tract disorders, most prevalent in females (urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, pelvic organ prolapse, recurrent urinary tract infection, and pelvic pain). Expert evaluation of these conditions includes a complete history and physical exam, as well as additional bladder studies such as Urodynamics (i.e. bladder function test), imaging studies (i.e. CT Scan and/or MRI), and cystoscopy.
Common Female Urology Conditions:
- Urinary Incontinence : Urinary incontinence is the medical term for accidental bladder leakage. This condition is more common in older women, and is not a normal part of aging.
- Symptoms
1. Leak urine when you laugh, cough, or sneeze - 2. Common in women who have had a baby
- Symptoms
- Overactive Bladder : Overactive bladder is the sudden, urgent need to urinate. Sudden urination may occur at any time of the day.
- Symptoms
- 1.Urinating more than 8 times per day
- Symptoms
2. The need to urinate at night
3. Sudden urges to urinate
4. May also be experiencing urinary incontinence (leakage)
- Recurrent Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
Urinary tract infections (UTI) occur when bacteria gets into the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside). These bacteria infections can occur in either the bladder or kidney. A UTI is considered recurrent when the patient experiences an infection more than 2 times in a 6 month period, or more than 3 times in one year.
Bladder Infection Symptoms
- Pain or burning when urinating
- Frequent/Urgent need to urinate
- Blood in the urine
Kidney Infection Symptoms
- Fever (Temperature over 99.9°F)
- Pain in one or both sides of the back
- Nausea or vomiting
- Interstitial Cystitis / Pelvic Pain
Interstitial cystitis, also called “bladder pain syndrome,” is a condition that causes people to have bladder pain and need to urinate often. This condition is more common in women, and doctors suspect that it is caused from abnormal changes in the lining of the bladder.
Symptoms
- Bladder pain that gets better after urinating
- Feeling like you need to urinate (even if you do not actually urinate)